Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) may be recommended for women experiencing symptoms during the menopause transition. The treatment works by increasing natural hormone levels that decrease during menopause — specifically estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone. HRT comes in different forms, including creams, patches, oral tablets, and more. It can also be administered using small implants known as hormone pellets.
Hormone pellets were clinically introduced in 1949 to increase estrogen levels in patients who had undergone hysterectomies.(1) The therapy became more widely recognized in the U.S. in the 1990s. While it’s not recommended for all patients, understanding how hormone pellets work can help women and their healthcare providers decide which form of HRT may be most appropriate.
What are hormone pellets?
Hormone pellets are small implants that are surgically placed under the skin. They are primarily used to treat symptoms of menopause, address testosterone or estrogen deficiency, or provide gender-affirming care for transgender men.(1)(2)(3) The size of hormone pellets can vary, typically measuring several millimeters (mm), with some as small as a grain of rice.(2) The size, shape, and surface area of hormone pellets are all relative to the dose.
How does hormone pellet therapy work?
Rather than synthetic hormones, hormone pellets contain bioidentical hormones that mimic the chemical structure of hormones naturally produced in the body.(4) The pellets may contain a single hormone or different combinations of hormones with varying dosage strengths.
The types of hormones commonly used in hormone pellets include estrogens, progesterone, testosterone, dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), and pregnenolone.(2)(5) Over several months, these pellets release hormones continuously into the body at a controlled rate as the implant gradually dissolves.(2) This method remains effective for three to six months, making dosing more convenient for patients as it requires fewer doctor visits throughout the year.(2)(6) However, each visit will involve an invasive procedure. In contrast, HRT creams, capsules, and gels release hormones immediately upon application or ingestion.
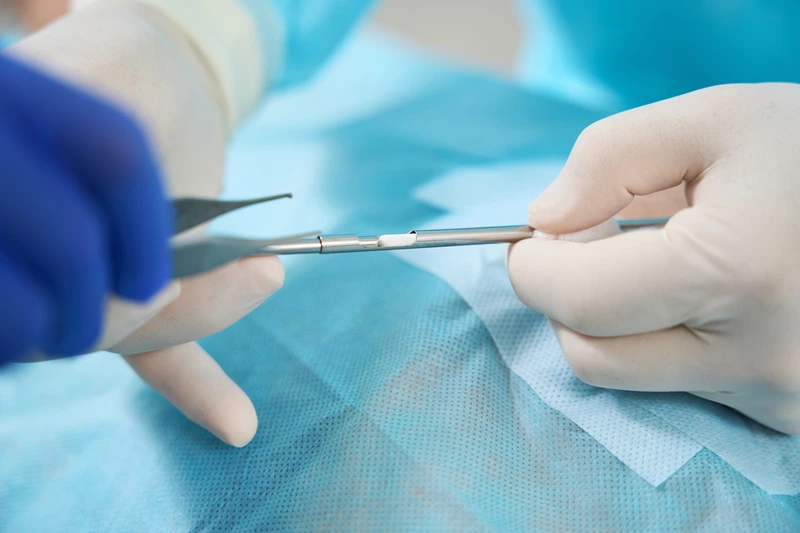
Surgical implantation of hormone pellets involves making a small incision in the lower abdomen, outer hip, or upper buttocks. A surgical tool is then inserted into the tissue to implant the pellet, after which the wound is closed with an adhesive strip.(1)(3)
Who might benefit from hormone pellet therapy?
Women experiencing menopause symptoms that interfere with daily life may benefit from hormone pellet therapy. These symptoms may include the following:(7)(8)
Hot flashes
Night sweats
Hormonal weight gain
Vaginal dryness
Mood changes
Pros and Cons of Hormone Pellets
Hormone pellets have both benefits and drawbacks. While they may offer more convenience, the surgical nature of hormone pellet therapy does pose risks of complications and potential side effects. Here are pros and cons of hormone pellet therapy:(1)(2)(6)(9)
PROS | CONS |
|---|---|
Fewer doses (every 3–6 months) | Minimally invasive surgical procedure |
Convenience: no daily pill reminders | Risk of surgical complications |
Potential for personalized dosing | Pain or irritation after insertion |
Better long-term compliance | Possible side effects |
Risk of overdose | |
Irreversible |
Negative Side Effects of Hormone Pellets
The following are potential side effects of hormone pellet therapy to consider:(1)(2)
Weight gain
Mood swings
Acne
Uterine bleeding
Breast tenderness
Hair changes
Abnormal lipid levels
Increased facial hair
Male pattern baldness
Voice changes
Clitoromegaly (abnormal enlargement of the clitoris)
Because hormone pellets cannot be removed once inserted, patients may continue to experience side effects for several months until the implant dissolves.
Other HRT Alternatives to Hormone Pellets
A medical provider may recommend alternative HRT options, such as oral medications like tablets, capsules, or lozenges. Topical hormone products, including gels, creams, and sprays, are also commonly used. Vaginal inserts, transdermal patches, and hormone injections are additional alternative treatments to hormone pellet therapy.(2)
Every HRT option affects the body differently, with varying impacts on metabolism, sexual health, and cardiovascular health.(10) Individuals should consult with a healthcare provider to determine which HRT options best meet their unique health needs.
Below are examples of different HRT alternatives to hormone pellet therapy:
Hormone Creams (Vaginal/Body/Facial Cream)
Hormone Pills (Tablets/Capsules)
Hormone Patches
Hormone Injections
Hormone injections may be in the form of suspensions or oil-based solutions.(1)(2)
Why Choose HRT Alternatives over Hormone Pellets?
Pills, creams, and patches containing bioidentical hormones — natural hormones with the same molecular structure as those produced in the body — can help alleviate common menopausal symptoms, such as sleep disruptions, night sweats, hot flashes, and more. These bioidentical HRT alternatives may be preferable to hormone pellets because they can be easily discontinued in the event of side effects; they do not pose the risk of surgical complications; and they ensure consistency in dosing.
However, when it comes to choosing between hormone pellets or HRT alternatives, individuals should speak with a healthcare provider about which form of HRT may be best suited to their needs.
